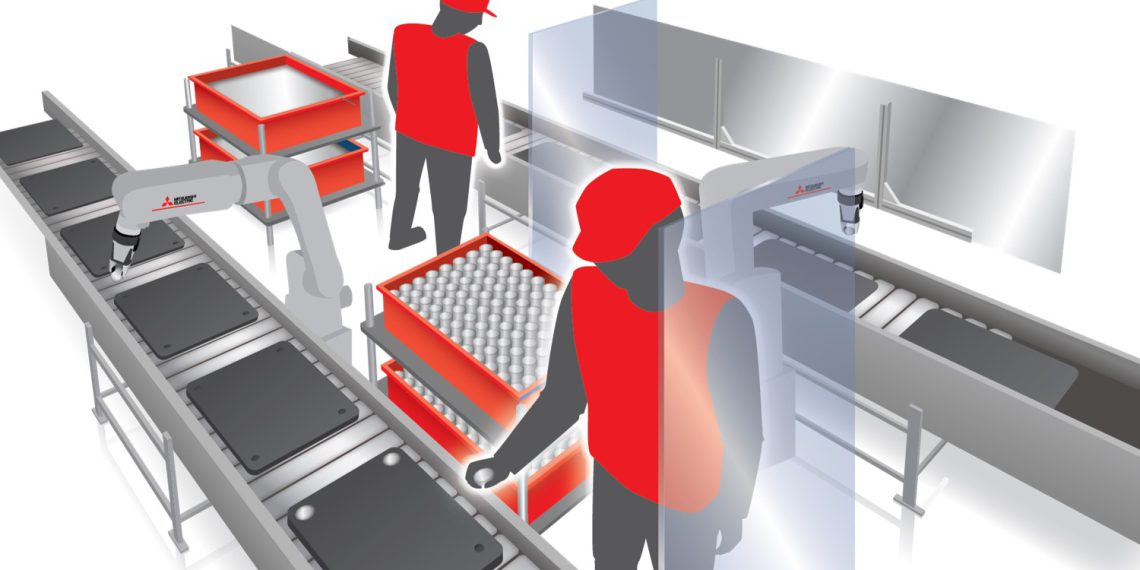
Increasing competition, often global, is forcing many manufacturers to become even more responsive to customer needs. In practice, this often means reducing batch sizes down to 1 and has brought with it the rise of “high-mix-low-volume” production. This is where cobots come into play. That’s because these collaborative helpers can enable manufacturers to effectively meet individual customer requirements with a greater variety of products in smaller batches.
High-volume production, with its repetitive tasks, still relies on traditional industrial robots. But in a high-mix production environment, there should be a rethink, because the time needed for programming and reconfiguration when changing products significantly affects productivity. This can be significant in high-mix production, where multiple line changes are required in a single shift.
 For many manufacturers, this has meant an increased reliance on manual labor. But that, in turn, increases operating costs compared to high-volume production — and the larger the mix, the higher the percentage of manual labor and the higher the production costs for a given run.
For many manufacturers, this has meant an increased reliance on manual labor. But that, in turn, increases operating costs compared to high-volume production — and the larger the mix, the higher the percentage of manual labor and the higher the production costs for a given run.
High-mix low-volume (HMLV) production requires more stringent quality control processes, as the risk of production errors increases as batch sizes decrease. At the same time, the number of changeovers between different products can often become a bottleneck.
However, the new generation of collaborative robots responds to the trend of HMLV production, providing the flexibility needed and the ability to reconfigure processes quickly and easily.
Improved flexibility, precision and reliability
These helpers are designed to assist human operators on the shop floor by performing simple, repetitive and physically demanding tasks. This provides improved consistency and reliability on the shop floor while allowing humans to focus on more complex tasks. A cobot is also flexible and can quickly learn to adapt to a variety of tasks, from pick-and-place to machine operation.
A key advantage is ease of programming, which allows frequent reuse and quick setup without robot programming expertise. A more recent development that can improve the simplicity and speed of configuration is hand-guided teaching. Here, the arm is simply moved to the desired position with the push of a button and added to the workflow. This eliminates the need for complex programming. It can also be combined with graphical touchscreen interfaces to implement more sophisticated operations.
A digital twin is suitable for faster retooling and recommissioning. It creates a digital image of the physical robot so that its performance can be evaluated virtually. The digital twin also simulates the robot’s interaction, ensuring it can safely and reliably perform the desired task before deployment.
The key to reducing operating costs
This ease of programming and changeover is a key enabler of HMLV production and the key to reducing operating costs. At the same time, the increased accuracy of the latest cobots is an important contribution to improving quality in a high-mix environment. Mitsubishi Electric’s MELFA ASSISTA cobots, for example, offer repeatability of ±0.03 mm, making them suitable for even the most demanding and precise tasks.
As manufacturers transition to HMLV production, they are finding that they can differentiate themselves from the competition by offering products tailored to specific customer requirements, even for the smallest batches. With the ability to quickly switch production to a different product, manufacturers are better able to respond to changes in the market, providing an additional competitive advantage.
These helpers are proving to be an important enabler for high-mix automation while providing maximum ROI. In an HMLV production environment, cobots increase flexibility and reduce operating costs.