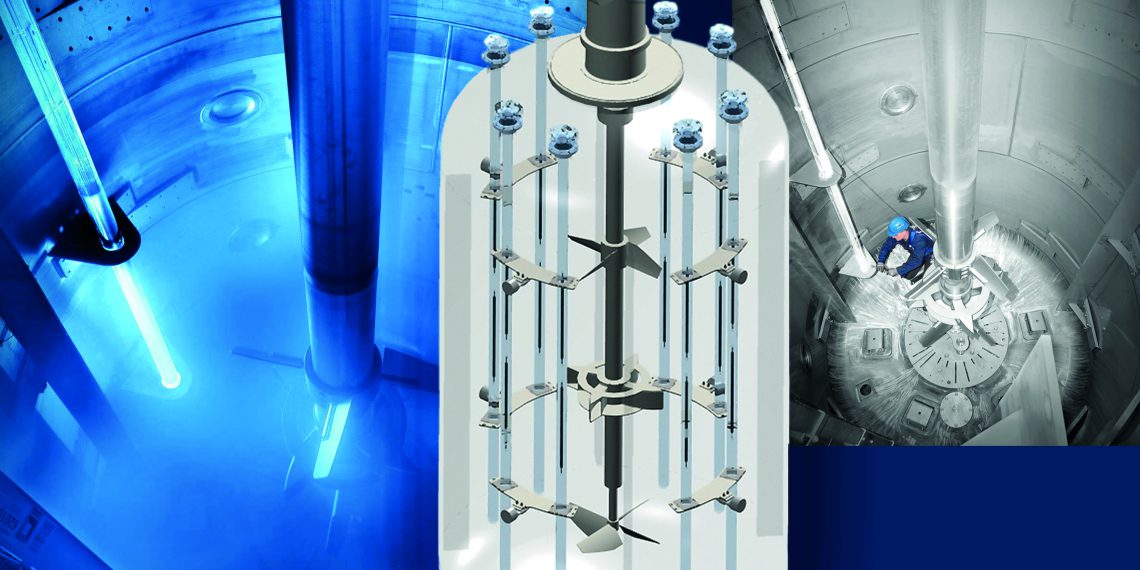
Chemical reactions need activation energy. Catalysts reduce this energetic barrier, but the catalyst as an additional component is expensive, often toxic and pyrophoric. Light is an alternative source of the activation energy. Photochemical reactions can be initiated by irradiation with wave lengths of 200 to 700 nanometers. This allows lower reaction temperatures with finally less decomposition or by-products. Examples of industrial photo reactions are chlorinations, sulfonations, sulfoxidations or nitrosylations. The concept of the new agitated reactor is ideal for multiphase reactions with liquid, gases and solids. It combines high productivity and flexibility with a reliable operation of the submerged light sources. Reactor sizes up to 50 m³ or beyond can be realized with the proven design.
The light sources are mercury or LED lamps submerged into the reaction mass inside a quartz glass tube. The glass tubes pass through nozzles in the tank head, where they connect to the power supply and the cooling medium. They need a hermetic sealing and monitoring to ensure that the unexpected case of a glass breakage is immediately detected. Their support must avoid local stress, allow for thermal expansion and prevent from vibration initiated by the intense agitation. As the power of the UV-lamps ranges from 5 to 60 kW each, the lamps need to be cooled inside the quartz tubes, otherwise high surface temperatures could damage the products. Industrial reactors can be equipped with 4 to 20 of such quartz tubes.
The penetration depth of the light into the reaction mass is short. Thus, the agitator has to provide high pumping rates and thereby a permanent renewal of the reactants in the irradiation zone. If one of the reactants is a gas as Cl2, O2 or SO2, it must be efficiently dispersed to achieve a maximum mass transfer for high conversion rates. The homogeneous suspension of solids as polymers, and the removal of the reaction heat have to be considered as well in the design of the agitator and tank.
The sealing of the agitator shaft towards the atmosphere is a key element for a reliable operation. Double or triple acting mechanical seals or hermetic magnetic drives are applied. Materials of construction of agitated photo reactors are steel with the option of glass lining, alloys or titanium.
Biogas technologies for production of biomethane
The untapped feedstock potential for biomethane production in Spain is very large as the country has a very strong food...
Read more